From intricate 3D architecture models to lush 3D environment models, the application of 3D modeling is vast and varied, serving sectors that demand the utmost accuracy and realism in their visualizations.
Exploring the Impact of 3D Modeling Across Industries
The advent of 3D modeling has marked a pivotal turn in how industries across the board plan, design, and present their projects. This innovative technology offers:
- Precision and Detail: Through 3D architecture models and 3D building models, every nuance of a project can be meticulously crafted and reviewed.
- Visualization: 3D environment models provide a realistic depiction of how projects will integrate with their surroundings, including 3D model trees and 3D models of plants for a complete environmental simulation.
- Efficiency: The ability to detect and correct issues in the design phase saves time and resources.
- Engagement: Enhanced presentations of designs that captivate and communicate effectively with clients and stakeholders.
In this context, 3D modeling is not just a tool but a fundamental component that has reshaped the landscape of design and presentation methodologies in various industries.
Architecture and Urban Planning
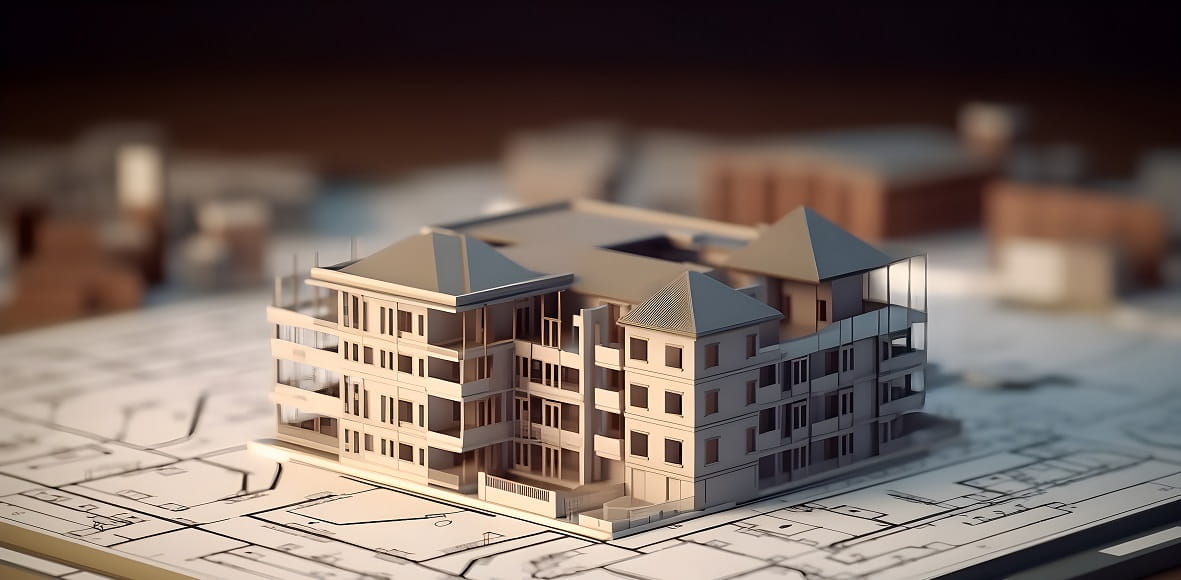
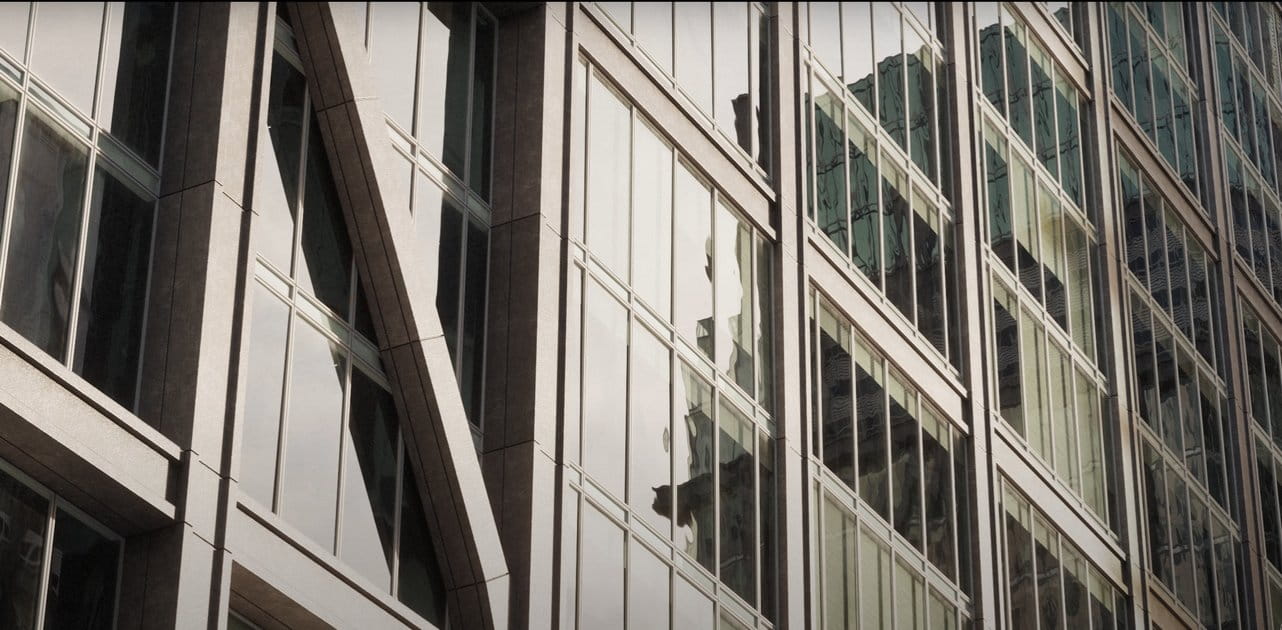
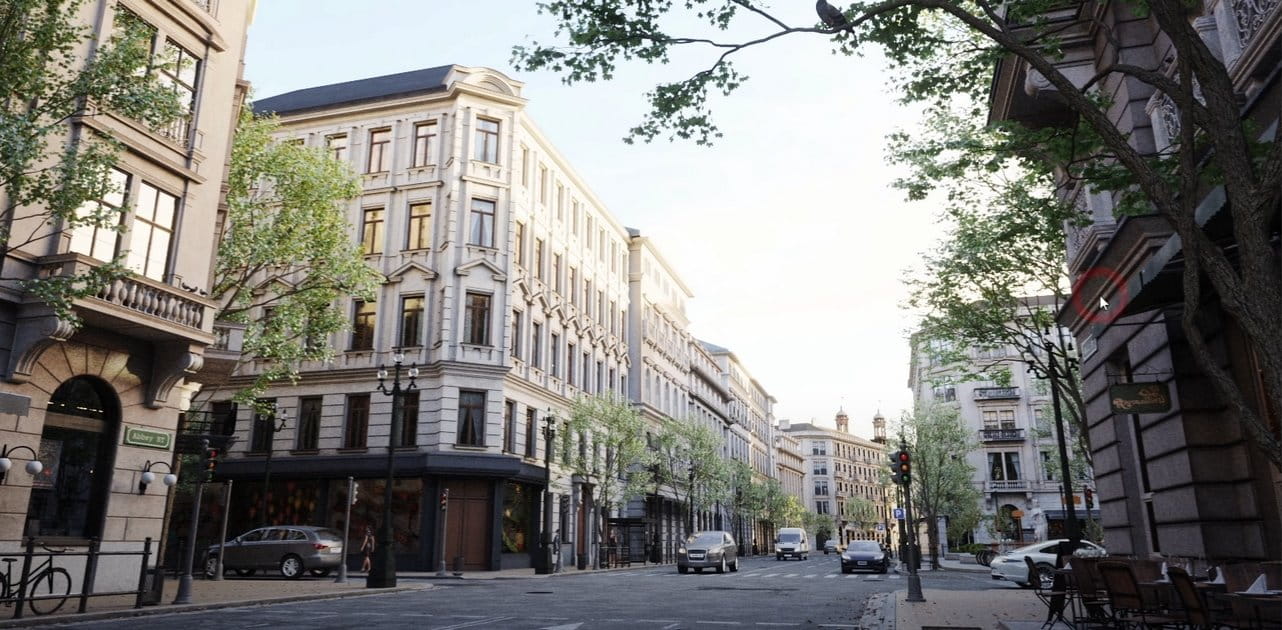
The capabilities of 3D modeling have profoundly impacted the field of architecture and urban planning. 3D architecture models and 3D building models are now fundamental in the design and planning stages, allowing architects and planners to visualize constructions in the context of their surrounding environments with unparalleled detail. Incorporating 3D model trees and 3D models of plants into these models provides a comprehensive view of how new structures will integrate with natural landscapes, promoting more sustainable and aesthetically pleasing designs. This level of detail assists in identifying potential issues early in the planning process, saving time and resources by enabling adjustments before physical work begins. Furthermore, these models facilitate stakeholder engagement, allowing non-professionals to effectively understand and contribute to the design process.
The use of 3D modeling in urban planning extends beyond individual buildings, encompassing entire cities and neighborhoods. Planners can simulate traffic patterns, pedestrian flow, and the impact of new developments on existing infrastructure. This predictive capability is crucial for creating functional spaces conducive to well-being and community interaction. By enabling a holistic view of urban development projects, 3D modeling supports more informed decision-making, leading to environments that are better suited to meet the needs of their inhabitants.
Real Estate and Marketing
In the competitive realm of real estate, 3D modeling has become a game-changer for marketing and sales strategies. 3D building models and 3D environment models offer prospective buyers a virtual walk-through experience, showcasing properties dynamically and engagingly. This elevates the presentation of properties and broadens the reach to potential buyers, transcending geographical limitations. 3D models help buyers make informed decisions by visually representing spaces, enhancing customer satisfaction and trust in the process.
This technology also allows for the customization of marketing materials, enabling real estate professionals to tailor their offerings to specific audiences. High-quality visuals can be created for print and online platforms, improving the overall impact of marketing campaigns. Additionally, 3D modeling facilitates the exploration of different design and furnishing options, allowing buyers to personalize their potential homes and connect more deeply with the property. This level of interaction and personalization is invaluable in today's market, where buyers seek more than just a space—they seek a vision of their future home.
Landscape Architecture
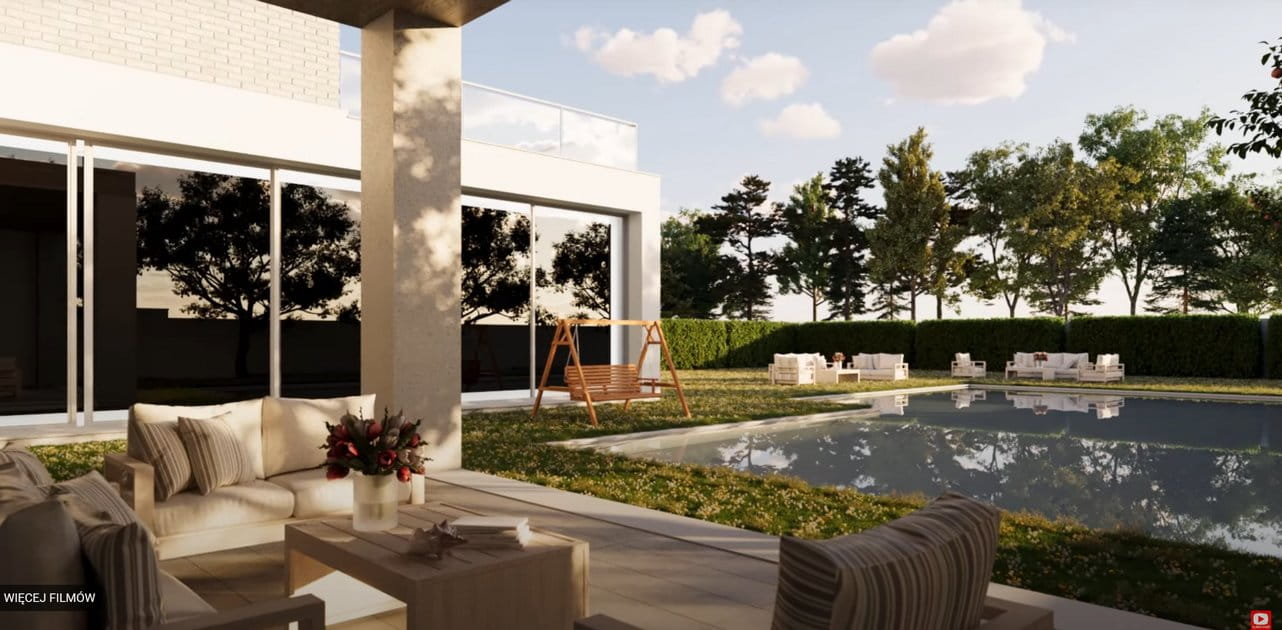
Landscape architecture benefits immensely from 3D modeling, with professionals using it to design and visualize outdoor spaces that are both beautiful and sustainable. 3D model trees, 3D models of plants, and comprehensive terrain analyses enable landscape architects to create designs that are in harmony with the natural environment. These models consider various factors such as soil type, water resources, and biodiversity, ensuring that designs contribute positively to the ecosystem. Moreover, 3D modeling allows for the simulation of environmental conditions, enabling designers to foresee how landscapes will evolve over time. This predictive insight is crucial for planning spaces that are resilient to climate change and other environmental challenges.
Applying 3D modeling in landscape architecture also enhances public participation in the design process. By presenting projects in a visually appealing and understandable manner, stakeholders can provide more meaningful feedback, leading to designs that truly reflect the needs and desires of the community. Furthermore, these models are effective tools for securing funding and approvals from regulatory bodies, as they clearly demonstrate the project's benefits and feasibility.
Interior Design
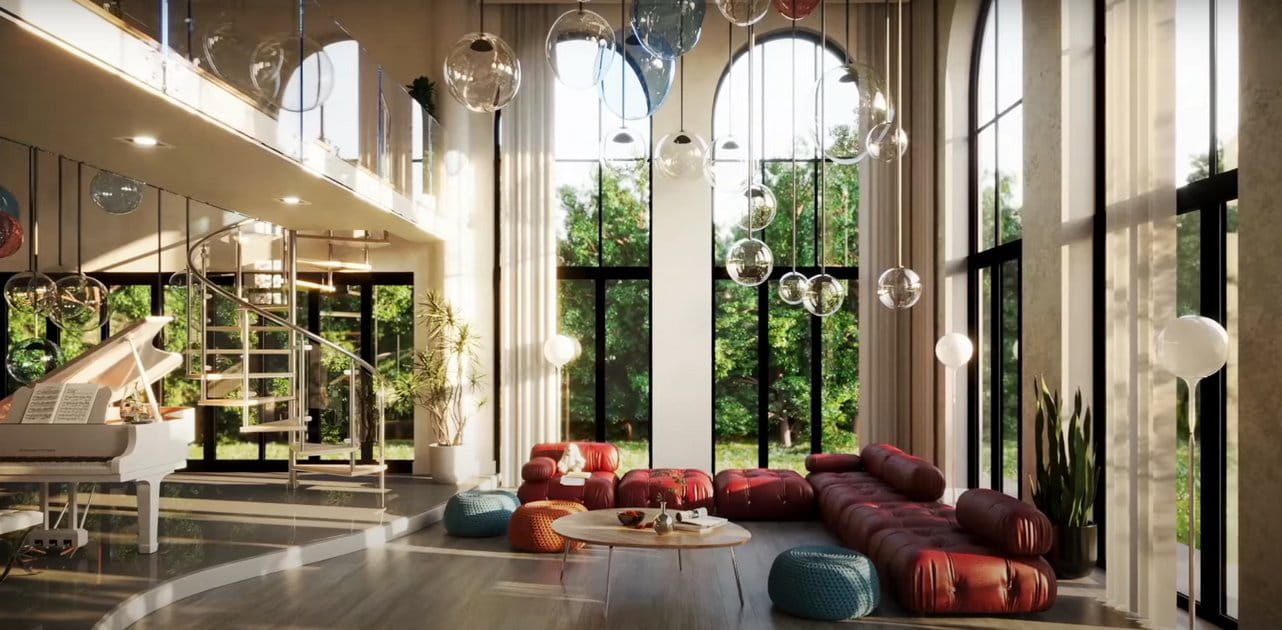
3D modeling has revolutionized the field of interior design, offering unprecedented creative freedom and precision. Designers utilize 3D architecture models to create detailed interior spaces, experimenting with furniture placement, color schemes, and lighting effects. This immersive approach allows clients to visualize the final look of their spaces, facilitating a collaborative design process. The ability to modify designs easily in the virtual realm reduces the likelihood of costly changes during construction, ensuring that projects stay within budget and meet deadlines.
Moreover, 3D modeling enables the exploration of innovative design solutions, pushing the boundaries of what is possible in interior spaces. Designers can experiment with custom furniture pieces, unique materials, and advanced lighting systems, creating interiors tailored to their clients' specific needs and preferences. This level of customization enhances the functionality and aesthetic appeal of spaces, leading to environments that truly reflect the individuality of their occupants.
Environmental Science
3D environment models are invaluable research, conservation, and planning tools in environmental science. These models facilitate the study of ecosystems, allowing scientists to simulate the effects of various factors such as climate change, pollution, and land use changes on natural habitats. 3D models help formulate strategies to protect and restore ecosystems by providing a detailed visualization of environmental processes. They are also crucial for the assessment of environmental impact assessments, enabling a thorough evaluation of how proposed developments might affect the natural environment.
The predictive power of 3D modeling is particularly important in the context of climate change, as it allows for the simulation of future scenarios. This enables researchers and policymakers to develop proactive strategies to mitigate the impacts of climate change on biodiversity, water resources, and human populations. Additionally, 3D models are used in environmental education, helping to raise awareness about the importance of conservation and sustainable practices.
Conclusion
As we have seen, 3D modeling is essential across various sectors, offering tools and technologies that drive innovation, efficiency, and sustainability. From architecture to environmental science, the ability to create detailed, accurate representations of the physical world opens up new possibilities for professionals and industries worldwide. As technology advances, the potential applications of 3D modeling are bound to expand, further embedding this indispensable tool in the fabric of our professional practices.
Customer zone
Your special offers
Your orders
Edit account
Add project
Liked projects
View your artist profile





















COMMENTS